Diagnostics Workflow, Verification & System-Level Validation
- chepqofficial
- Dec 19, 2025
- 3 min read
Updated: Dec 30, 2025
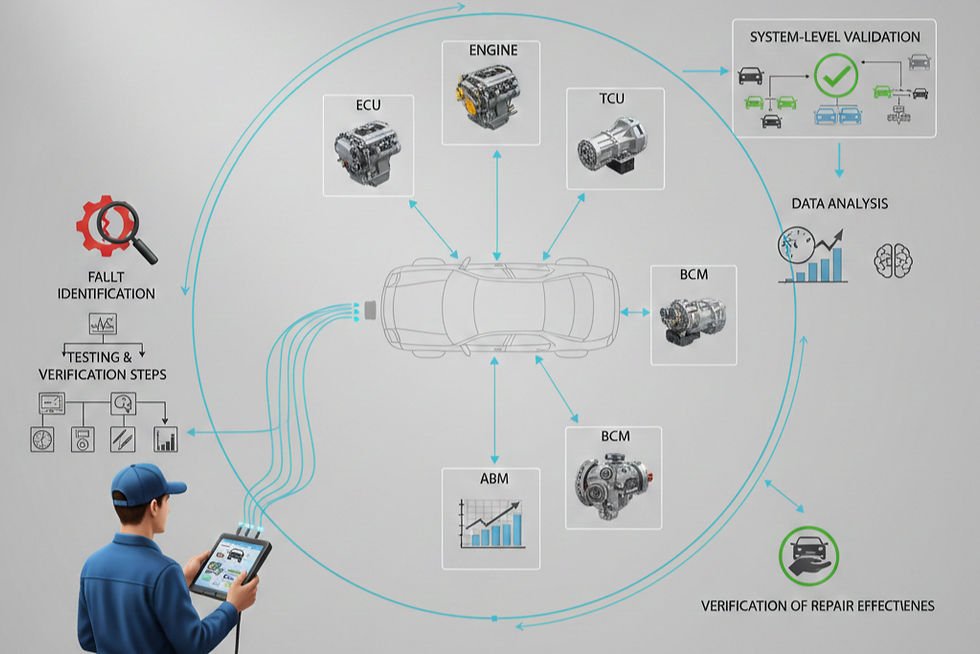
Accurate diagnostics is not a single measurement or test result. It is a structured workflow that moves from symptom observation to system verification, ensuring conclusions reflect actual vehicle behavior.
Diagnostic workflows organize data acquisition, interpretation, confirmation, and validation into a coherent process.
Diagnostic Workflow as a Control Process
Diagnostics follows a controlled sequence. Each step constrains interpretation and prevents premature conclusions.
Workflow discipline reduces noise, confirmation bias, and misattribution. Skipping steps compresses complexity at the cost of accuracy.
Diagnostics workflows formalize reasoning rather than replace expertise.
Symptom Definition and Context Establishment
All diagnostics begins with symptom definition. Observable behavior establishes system context before any tool interaction.
Symptoms define operating conditions, triggering scenarios, and temporal patterns. Without context, data lacks meaning.
Diagnostic workflow anchors measurement to real-world behavior.
Baseline Data Collection
Baseline data establishes reference conditions. This includes system states, environmental variables, and known-good parameters.
Baseline acquisition precedes fault isolation. Deviations gain meaning only relative to reference behavior.
Workflow integrity depends on baseline clarity.
Progressive Isolation Strategy
Diagnostics proceeds from system-level observation to subsystem isolation. Broad evaluation precedes targeted testing.
Isolation narrows fault domains without prematurely excluding interacting systems. Over-isolation obscures root causes.
Structured narrowing preserves causal relationships.
Signal Correlation Across Domains
Modern vehicles exhibit cross-domain interactions. Mechanical, electrical, network, and software layers influence one another.
Workflow validation correlates signals across domains to identify causal alignment rather than coincidence.
Correlation distinguishes symptom from source.
Temporal Validation and Repeatability
Single observations rarely confirm faults. Diagnostics requires repeatability under controlled conditions.
Workflow validation includes time-based verification. Faults must reappear consistently when conditions recur.
Repeatability separates transient noise from systemic issues.

Active Testing and Controlled Intervention
Active tests introduce controlled changes to observe system response. Actuation, adaptation resets, and forced states probe causality.
Workflow structure ensures interventions occur after observation, not before.
Controlled action validates hypotheses.
Data Interpretation and Hypothesis Testing
Interpretation converts measurements into explanations. Hypotheses emerge from observed patterns, not isolated values.
Workflow discipline requires hypotheses to be testable and falsifiable.
Diagnostics is an iterative reasoning process.
Fault Confirmation and Verification
Confirmed faults meet multiple criteria: repeatability, correlation, and response to intervention.
Verification ensures identified faults explain all observed symptoms, not just a subset.
Partial explanations signal incomplete diagnostics.
Post-Repair Validation
Repair actions alter system behavior. Validation confirms resolution under original symptom conditions.
Absence of faults without functional verification remains insufficient.
Workflow closure requires confirmation, not assumption.
System-Level Validation
Vehicles operate as integrated systems. Validation considers interactions beyond the repaired component.
System-level validation ensures no secondary effects emerge after intervention.
Holistic validation protects against cascading issues.
Diagnostic Documentation and Traceability
Diagnostics generates knowledge. Documentation preserves reasoning, observations, and outcomes.
Traceability supports future diagnostics, trend analysis, and accountability.
Workflow maturity includes record integrity.

Workflow Adaptation Across Technologies
EVs, ADAS, and connected systems expand diagnostic complexity. Workflows adapt but do not dissolve.
Structured reasoning scales across technologies.
Workflow consistency enables cross-platform diagnostics.
Human Factors in Diagnostic Workflow
Cognitive load, bias, and assumption influence diagnostics. Workflow structure mitigates human error.
Discipline complements experience rather than constrains it.
Human-centered workflow design enhances accuracy.
Diagnostic Workflow as Quality Control
Workflow validation functions as quality control for diagnostics. It ensures conclusions withstand scrutiny.
Reliable diagnostics emerges from process integrity, not isolated expertise.
Integration Within the Diagnostic Framework
This pillar integrates with:
Workflow coherence connects tools, data, and reasoning.


