ECU (Engine Control Unit)
The computer that controls fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions systems.
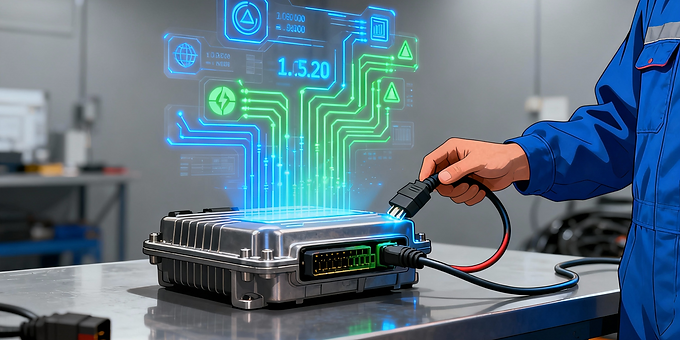
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is the brain of the modern vehicle. It processes sensor data to adjust fuel mixture, spark timing, and idle speed for maximum efficiency. ECUs monitor air-fuel ratio, throttle position, oxygen levels, and other signals to maintain performance and reduce emissions. When an issue occurs, the ECU logs diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) retrievable via an OBD-II scanner. Reflashing or reprogramming the ECU can improve performance or fix software bugs. Proper ECU diagnostics require understanding both electrical and software interactions.
Related Diagnostic Guide
This topic is part of CHEPQ’s system-level diagnostic framework.
For a broader understanding of how this component is analyzed in real-world diagnostics, refer to the following guide:
Applying This Knowledge in Practice
The diagnostic principles discussed above are commonly applied in real-world vehicle diagnostics. To put this knowledge into practice, explore professional automotive diagnostic tools designed to support system testing, fault analysis, and troubleshooting across modern vehicles.